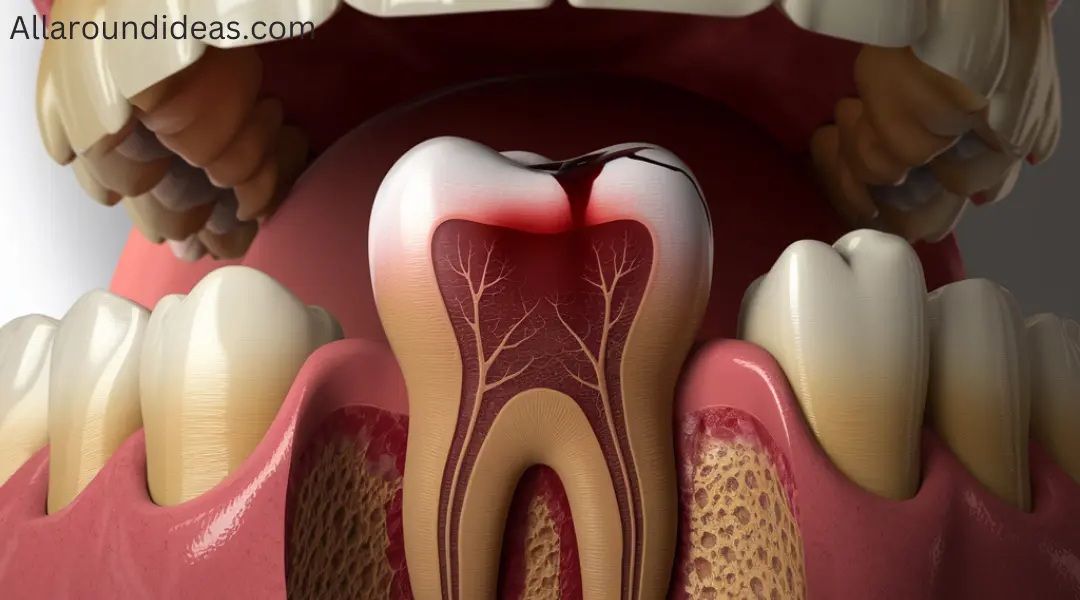
Introduction
A tooth infection, also known as a dental abscess, is a serious condition that can arise from untreated cavities, gum disease, or trauma to a tooth. While many people may think of tooth infections as merely a source of pain, they can lead to severe complications if not addressed promptly. One of the most alarming questions surrounding tooth infections is: how long until a tooth infection can lead to life-threatening consequences? In this article, we’ll explore the nature of tooth infections, their potential complications, and the factors that influence how quickly they can become dangerous.
If you want some more information about HVAC Tools then checkout our last blog post.
What Is a Tooth Infection?
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You, leading to the formation of pus. This can happen for various reasons:
- Untreated Cavities: Bacteria can penetrate through cavities that are not addressed in a timely manner.
- Gum Disease: Periodontal disease can create pockets around the teeth where bacteria thrive.
- Trauma: A broken or cracked tooth can provide an entry point for bacteria.
Symptoms of a tooth infection often include severe pain, swelling, fever, and a bad taste in the mouth. If left untreated, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues and even into the bloodstream, leading to more serious health complications.
The Timeline of a Tooth Infection
The timeline for how quickly a tooth infection can become life-threatening varies widely among individuals. However, several general phases can help illustrate the potential progression:
1. Initial Infection (Days to Weeks)
In the early stages, a tooth infection may manifest as localized pain and swelling. This can occur within a few days after the initial bacterial invasion. During this period, if you seek treatment—such as antibiotics or a root canal—you may effectively manage the infection without further complications.
If you want some more information about HVAC Tools then checkout our last blog post.
2. Spread of Infection (Weeks to Months)
If the infection is not treated, it can begin to spread. This phase might last several weeks to months, during which the infection can affect nearby teeth, gums, and even the jawbone. Common symptoms during this time include:
- Increased pain and swelling
- Fever and malaise
- Drainage of pus from the affected area
While the body’s immune system may initially fight the infection, prolonged exposure can overwhelm it, increasing the risk of severe complications.
3. Systemic Complications (Months to Years)
If the infection continues to progress without treatment, it can lead to systemic complications. This phase can take months or even years, depending on the individual’s health and the severity of the infection. Potential complications include:
- Sepsis: This is a life-threatening response to infection that occurs when the body’s immune system goes into overdrive. Sepsis can develop rapidly, sometimes within hours to a few days after the infection spreads to the bloodstream.
- Osteomyelitis: An infection of the bone, often resulting from a dental abscess that spreads to the jawbone.
- Ludwig’s Angina: A serious, potentially life-threatening infection that can cause swelling in the floor of the mouth and lead to airway obstruction.
Factors Influencing the Timeline
Several factors can influence how quickly a tooth infection can become life-threatening:
1. Individual Health
The overall health of the individual plays a significant role. Those with weakened immune systems—such as individuals with diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or undergoing chemotherapy—are at higher risk for rapid progression of infection.
2. Type of Bacteria
The specific type of bacteria involved can also affect the timeline. Some bacteria are more virulent than others and can spread more quickly. For instance, Staphylococcus aureus and certain strains of Streptococcus can be particularly aggressive.
3. Timeliness of Treatment
Seeking prompt dental treatment is crucial. The earlier an infection is treated, the less likely it is to spread. Antibiotics, drainage of abscesses, and surgical intervention can effectively manage and contain the infection.
4. Location of the Infection
Infections located in the upper jaw may spread to the sinuses, while those in the lower jaw can affect the neck and airway. The potential for these infections to impact vital structures can accelerate the risk of life-threatening complications.
Warning Signs of a Serious Infection
Recognizing the warning signs of a severe tooth infection is essential. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- Severe Pain: Pain that does not improve with over-the-counter medications.
- Swelling: Rapid swelling in the face or neck.
- Fever: A high fever, often indicating a systemic infection.
- Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: This could signal that the infection is affecting the airway or causing swelling in the throat.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately.
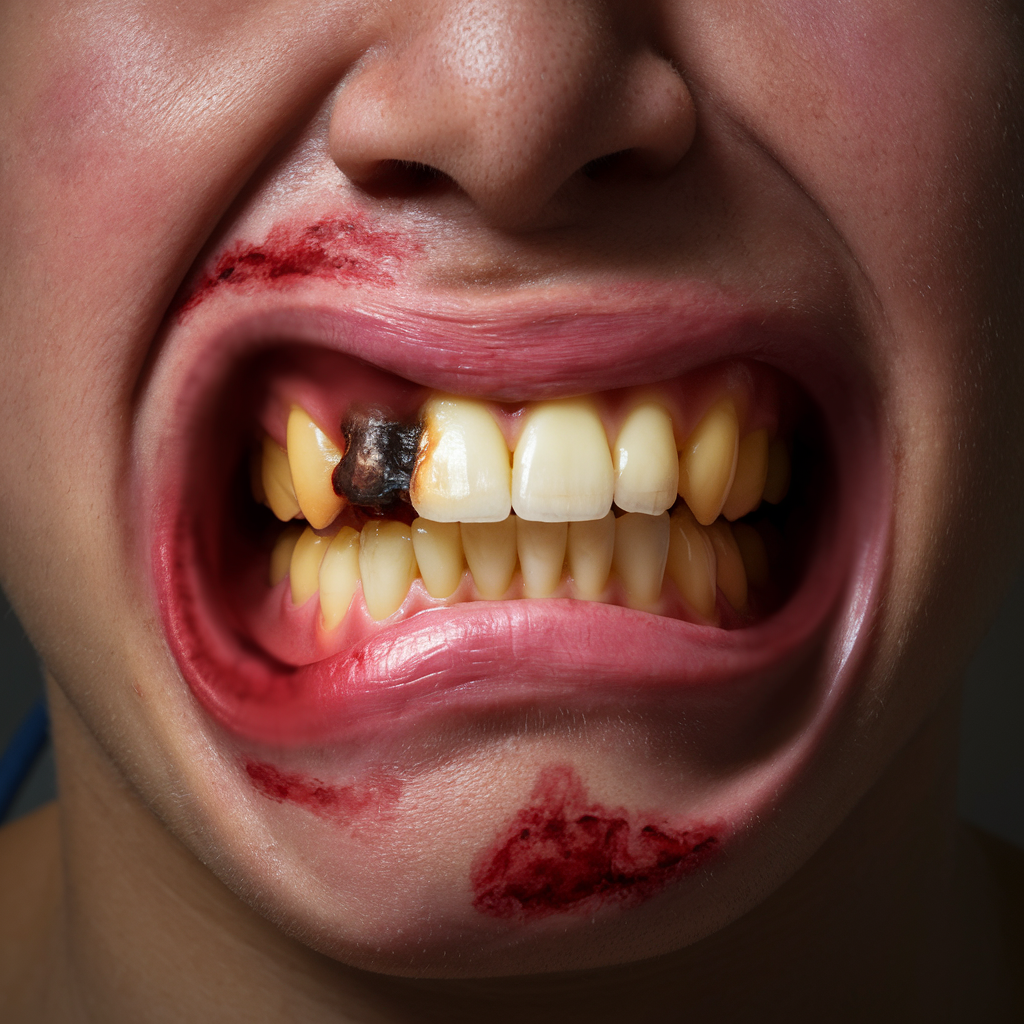

Consequences of Untreated Tooth Infections
The consequences of allowing a tooth infection to go untreated can be severe:
If you want some more information about HVAC Tools then checkout our last blog post.
1. Life-Threatening Conditions
As discussed, complications like sepsis and Ludwig’s angina can be fatal if not treated promptly. Sepsis, for example, can lead to multi-organ failure within a short time frame.
2. Long-Term Health Issues
Even if a person survives a severe infection, there may be long-term health issues, including chronic pain, difficulty swallowing, or speech problems due to damage to the jaw or throat.
3. Financial and Emotional Impact
The financial burden of emergency medical treatment can be significant. Additionally, dealing with the pain and complications of an untreated infection can have lasting emotional and psychological effects.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing tooth infections involves good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups. Here are some essential tips:
1. Maintain Oral Hygiene
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily.
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce plaque and bacteria.
2. Regular Dental Visits
- Schedule regular check-ups and cleanings with your dentist to catch potential problems early.
3. Address Issues Promptly
- If you notice signs of cavities or gum disease, seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent complications.

Conclusion
While a tooth infection can start as a manageable issue, it has the potential to escalate into a life-threatening condition if left untreated. The timeline for how long it takes for a tooth infection to become dangerous can vary widely, typically progressing from localized symptoms in days to severe complications over weeks to months. Individual health, the type of bacteria involved, and the timeliness of treatment are critical factors in determining the risk.
If you want some more information about HVAC Tools then checkout our last blog post.
Being aware of the symptoms of a tooth infection and seeking prompt dental care can significantly reduce the chances of severe complications. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are essential strategies for preventing tooth infections and protecting your overall health. If you experience any concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Your health is worth it.